Deploying a MERN Stack Application to Render
May 28, 2024This guide walks you through the steps required to deploy your MERN stack application to Render with a MongoDB database using MongoDB Atlas.
If you don't yet have a MongoDB Atlas account, please see Set Up MongoDB Atlas before you proceed.
First, you'll create a database for your application.
Navigate to the MongoDB Atlas dashboard. Click on the "Database" link in the left-hand sidebar. You'll see something like the following image:
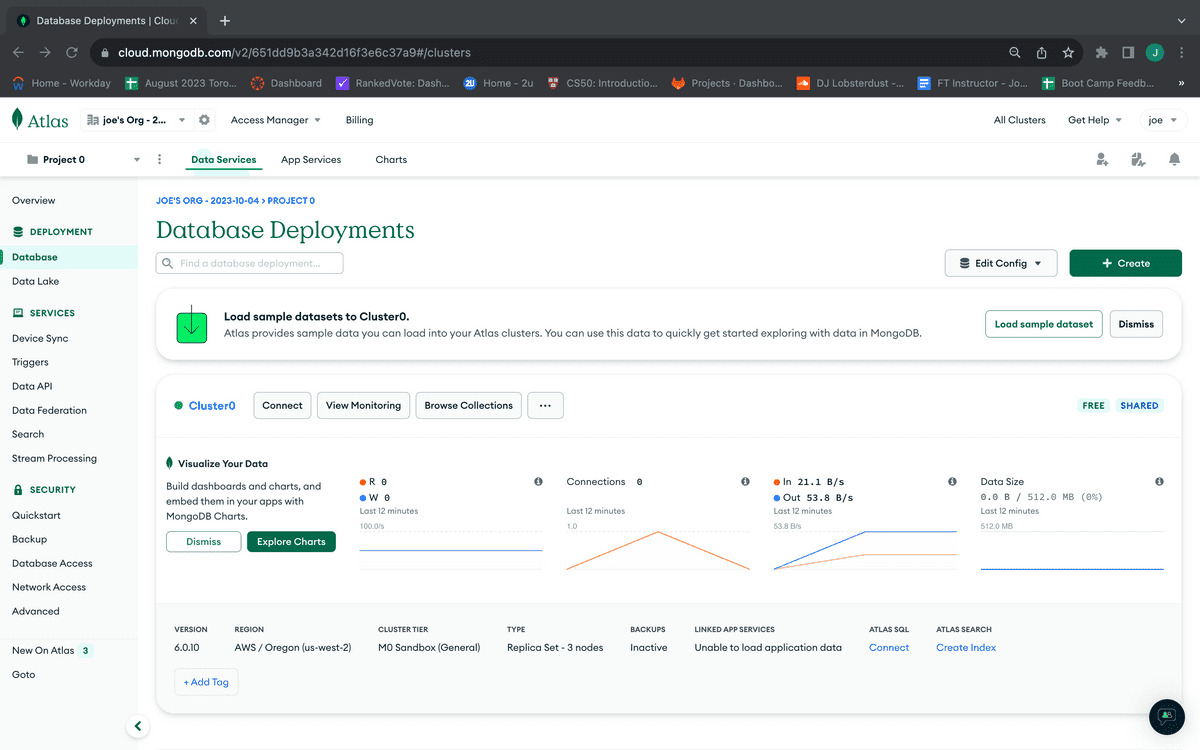
To create a database for your application, click the "Browse Collections" button in your sandbox Clusters box. If you haven't previously created a database, you'll be taken to a page that looks like the following image:
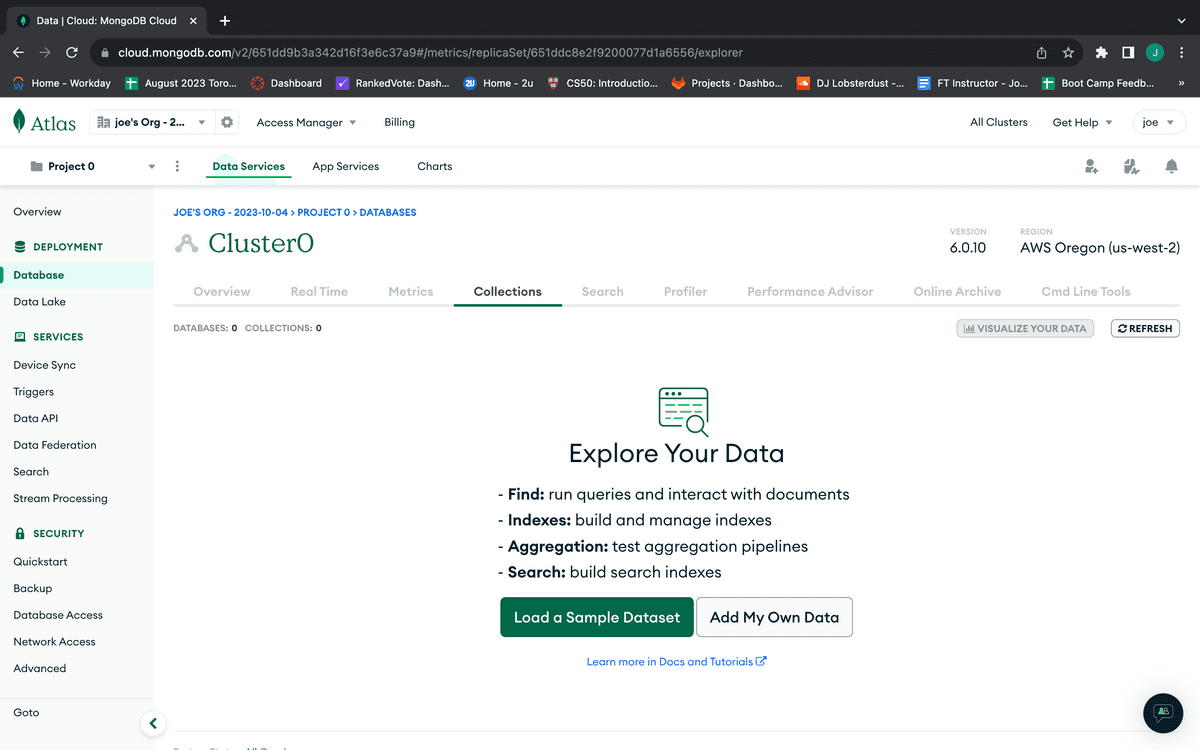
From this page, select the "Add My Own Data" button. If you previously created a database through MongoDB Atlas and need to create another one for this app, click the "+ Create Database" button in the left column of the window pane instead. Either way, the resulting modal should look like the following image:
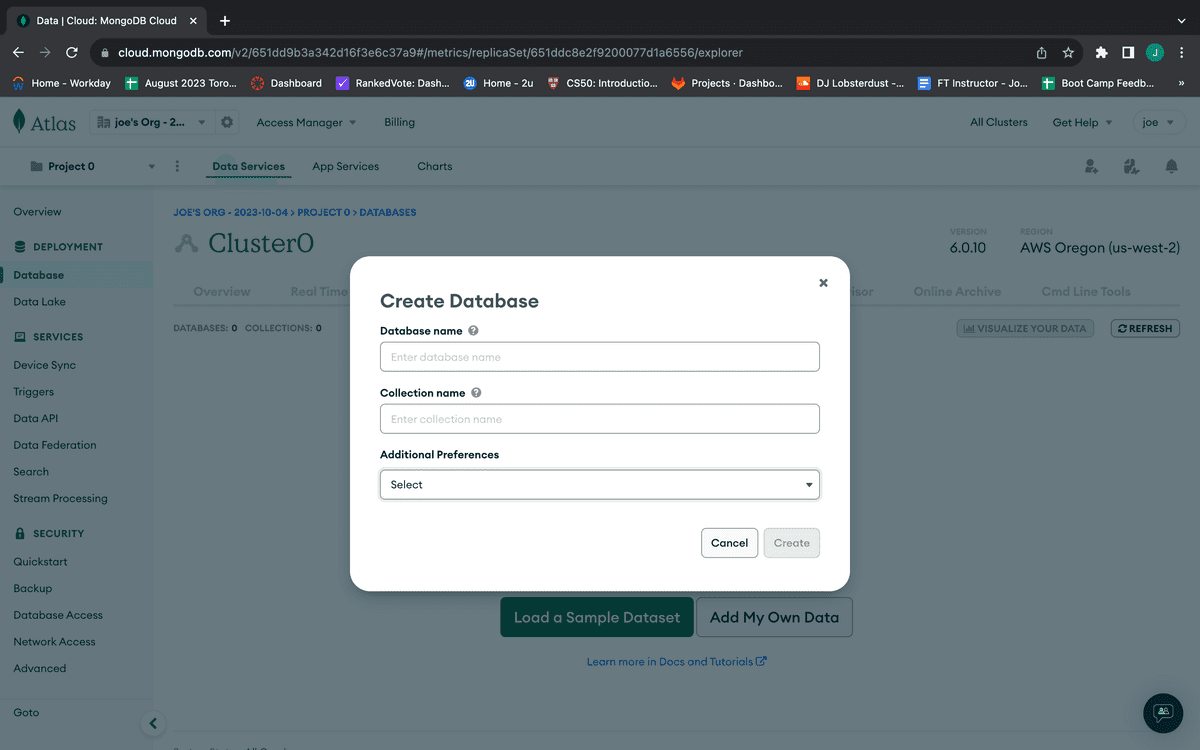
Fill out the form with the name of your MongoDB database and a collection for that database. Leave the "Additional Preferences" field blank. You only need to create one collection to get started, as your application will create them upon deploy, so don't worry if you think your database will scale up or down in the future.
When you're done creating your database and initial collection, the dashboard should display them, as shown in the following image:
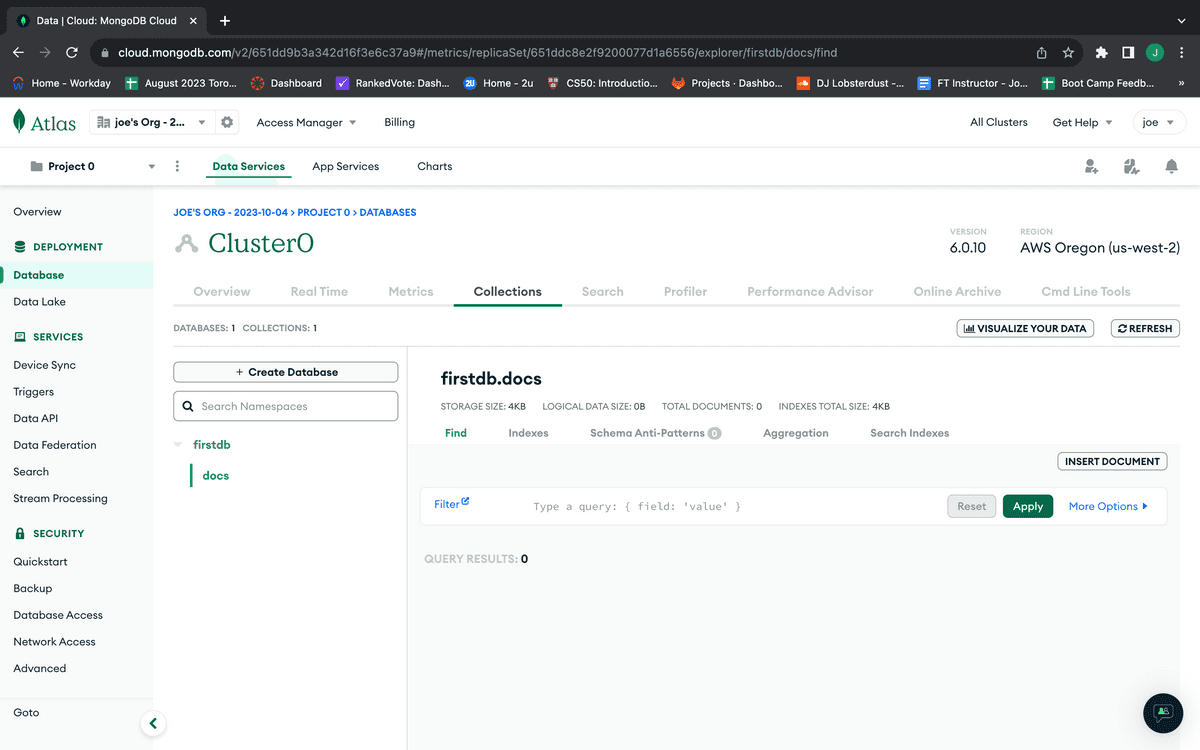
Great! Your database has been created. Let's move on to connect it to your application in production.
You've likely already deployed a front-end application to a platform like GitHub Pages. But to deploy an application with a back end, you'll need a platform like Render that can handle the additional configuration—so that your app can accept incoming connections from the internet.
To start, make sure that your project is initialized as a Git repository. You can check this by running the following command at the root of your project:
git status
If you encounter an error, that means that your project isn't yet a Git repository. You can initialize the repository by running the following command:
git init
Applications that feature an Express.js back end can use Render's PORT environment variable. To set this up, create a port variable with a value of process.env.PORT. You can also add a default value for local instances of your server by using the || syntax, as shown in the following example:
const port = process.env.PORT || 3001
Render allows you to deploy directly from a GitHub repository, so make sure you have committed and pushed your changes to your GitHub:
git add -Agit commit -m "<descriptive message here>"git push
Update the install script and add a render-build script to your package.json similar to the following example:
{"name": "googlebooks-app","version": "1.0.0","description": "","main": "server/server.js","scripts": {"start": "node server/server.js","develop": "concurrently \"cd server && npm run watch\" \"cd client && npm run dev\"","install": "cd server && npm i && cd ../client && npm i --production=false","build": "cd client && npm run build","render-build":"npm install && npm run build"},"keywords": [],"author": "","license": "ISC","devDependencies": {"concurrently": "^8.2.0"}}
Now that we've created the repository, configured the server, and pushed to GitHub, we can create an app on Render and link it to our existing GitHub repository.
The Render dashboard allows us to easily create an app and link an existing GitHub repository to it to deploy.
Create a new Render app by clicking the "New" button on the right side of the navbar, as shown in the following image:
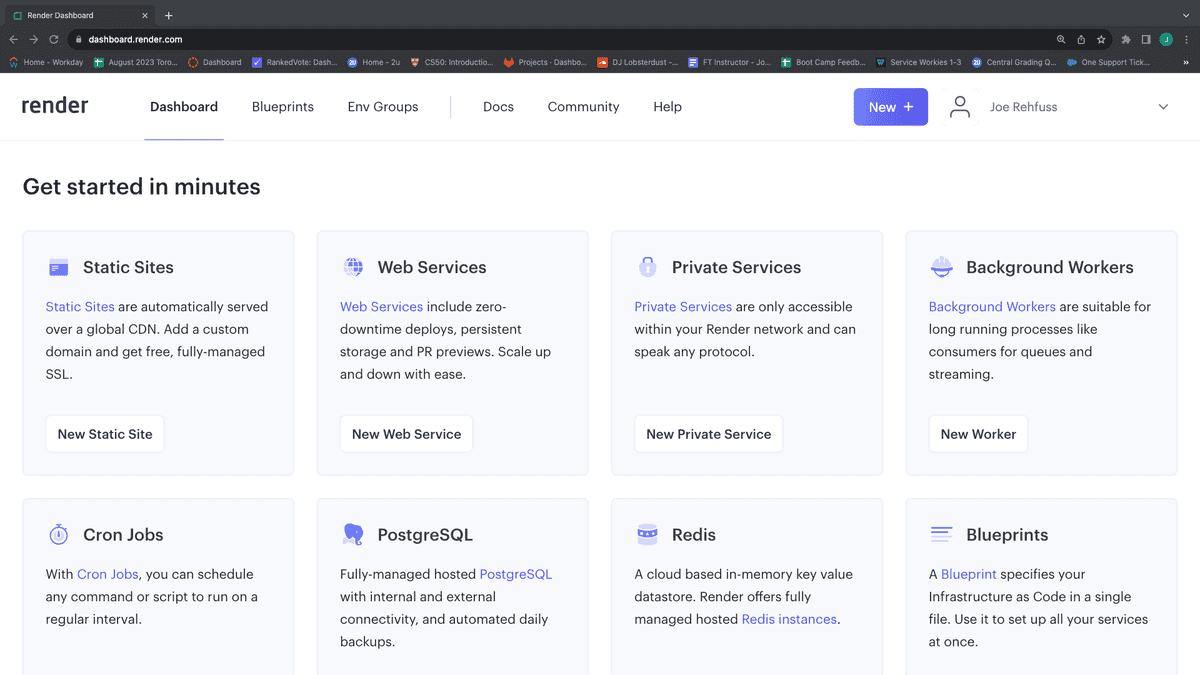
Select "Web Service" from the dropdown menu, as shown in the following image:
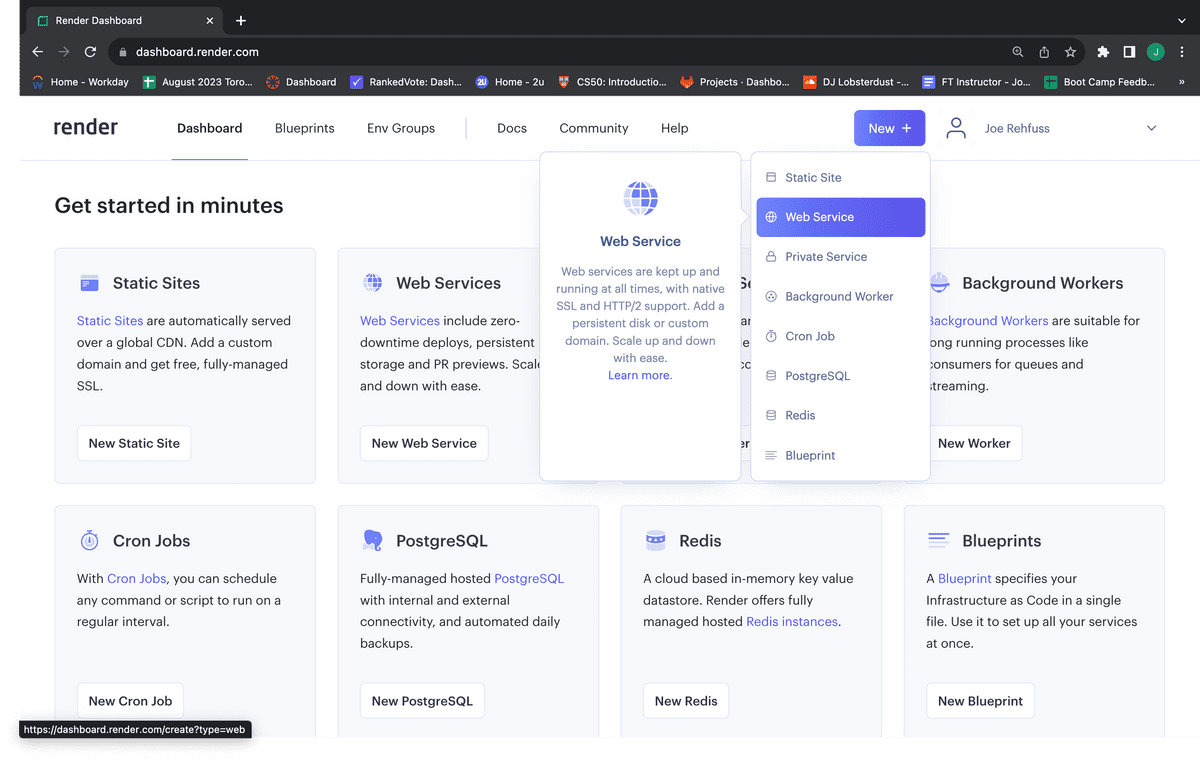
Make sure "Build and deploy from Git repository" is selected, then click "Next," as shown in the following image:
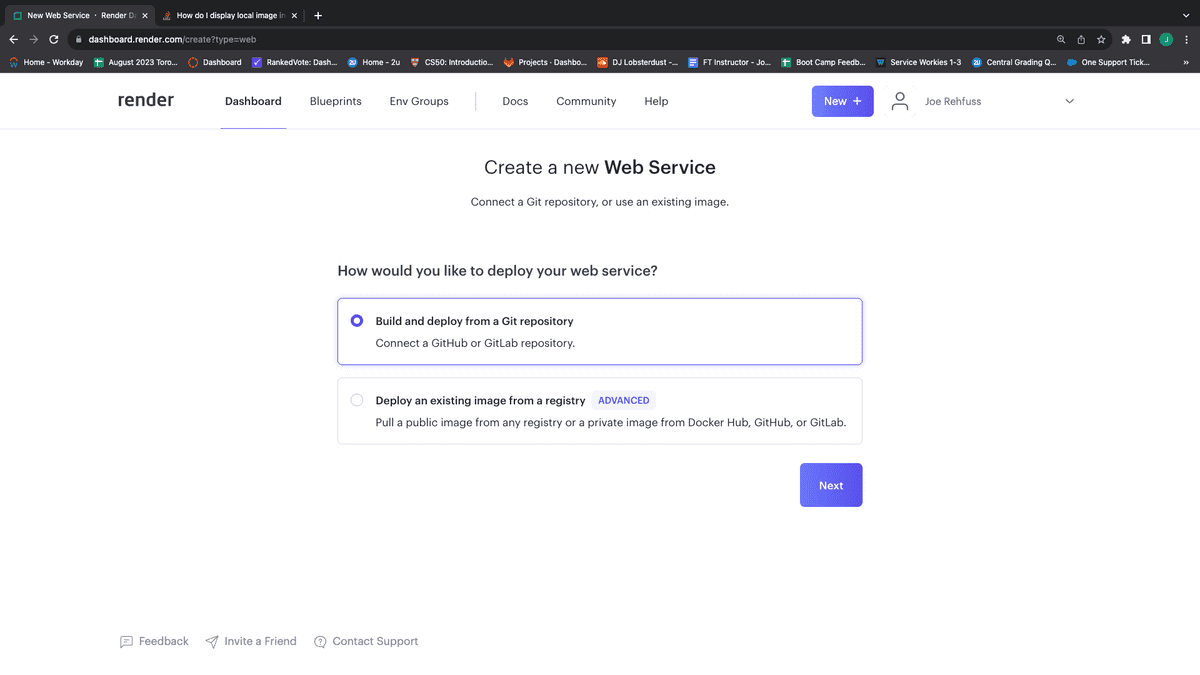
If this is your first time deploying to Render, you will need to allow access to your GitHub repositories. Click on the "+ Connect account" link under the GitHub heading, as shown in the following image:
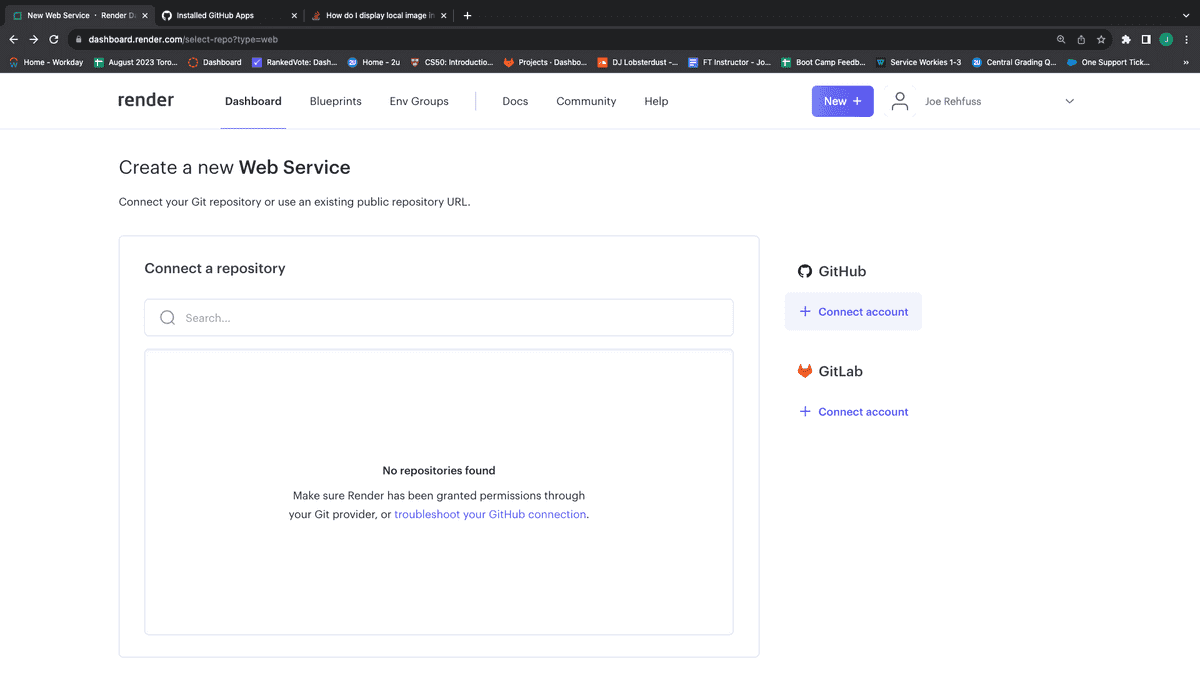
Next, install Render to your GitHub account, providing access to all of your repositories, as shown in the following image:
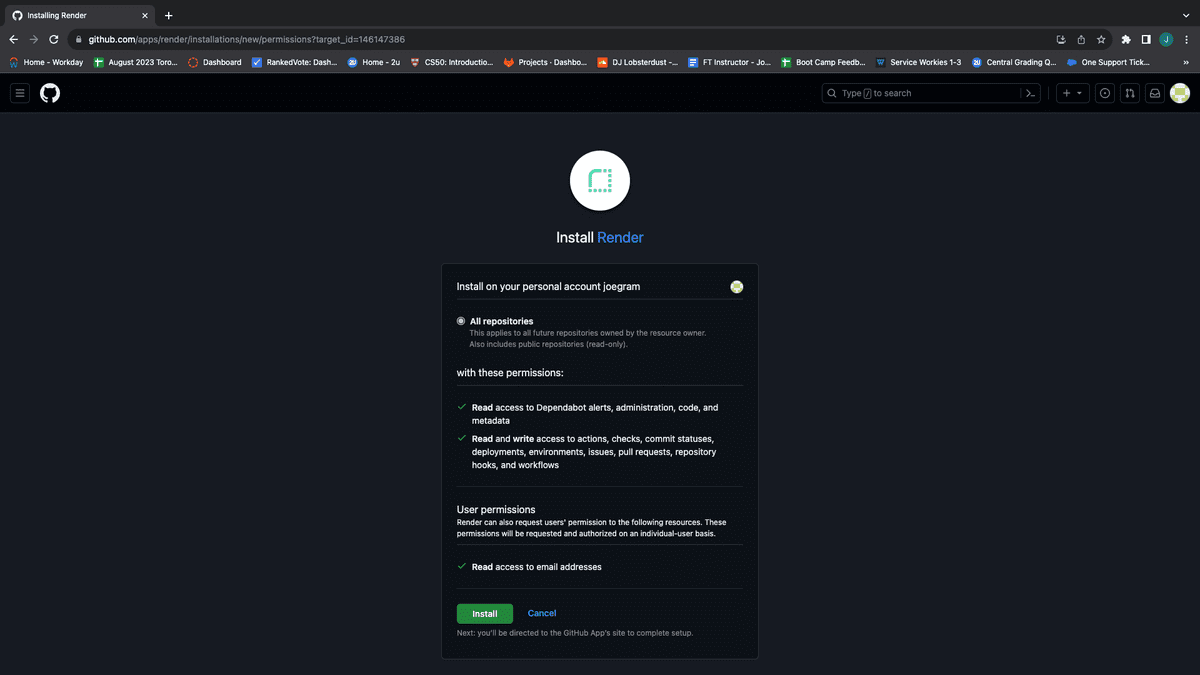
Click the blue "Connect" button next to the repo you want to deploy. You can use the search box to filter out the repo you want, as shown in the following image:
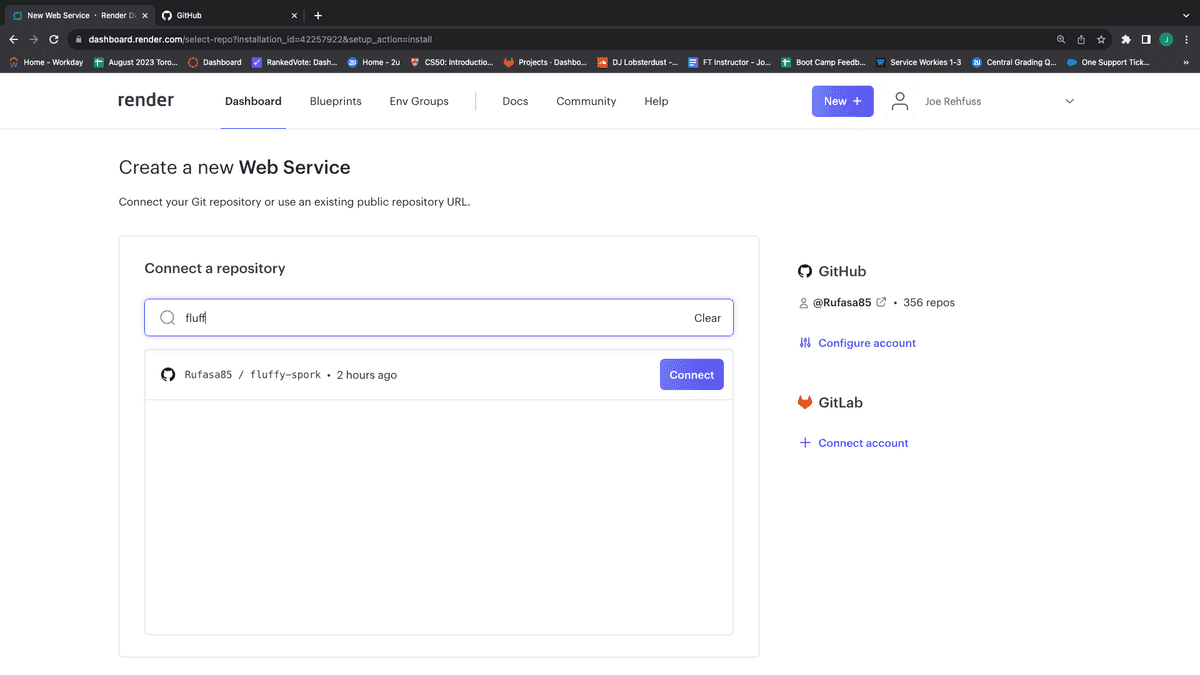
Give your new Render app a unique name, as shown in the following image. It does not have to match the repo name, but it is useful to do so to keep track of which app is attached to which repo:
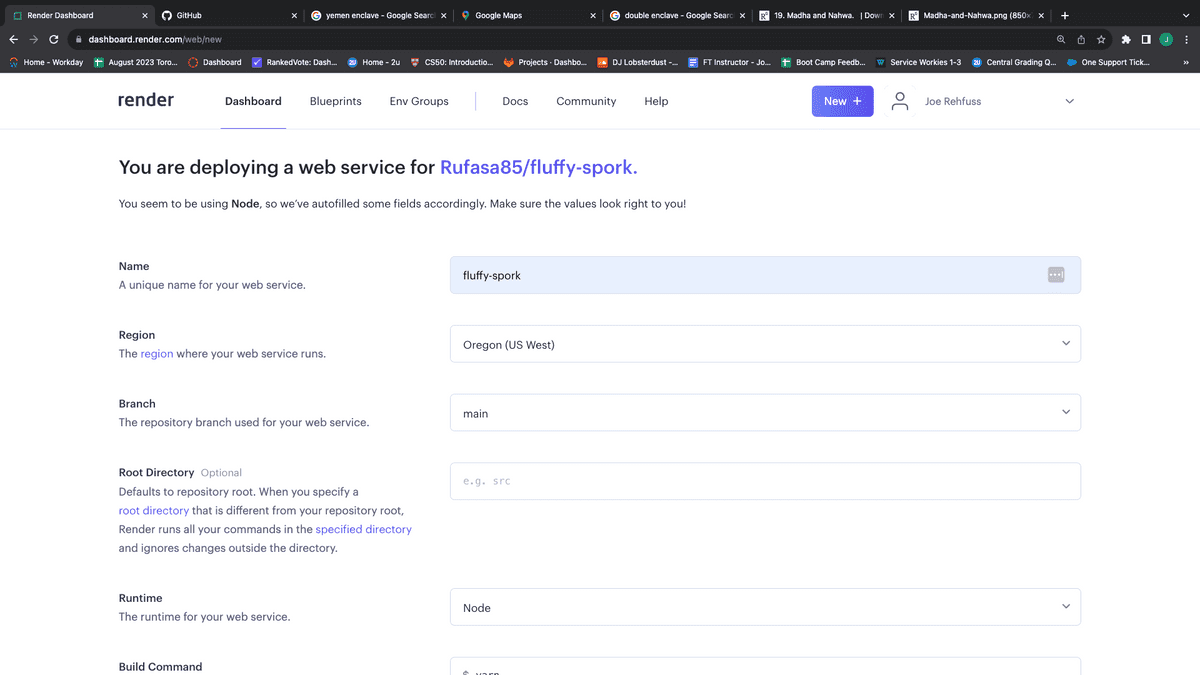
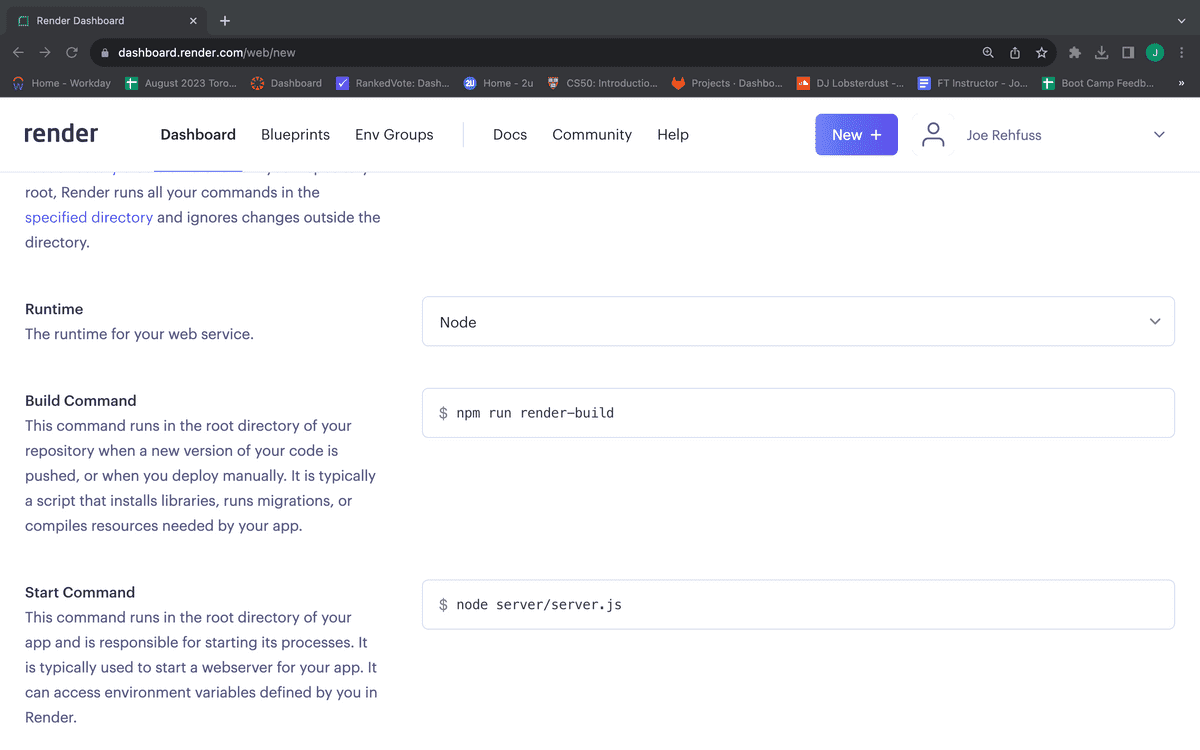
Render needs to know which steps need to be taken to get your app up and running. In the case of a MERN stack app, we need to run npm install to install all required dependencies and npm build to build compile the front-end of our application. We created a custom script, render-build, that will perform both of these tasks. Scroll to the section "Build Command" and update the field to npm run render-build. Render also needs to know which command to run to start your application. The "Start Command" field will be automatically populated with the start script from your package.json. Confirm that the "Start Command" is correct, as shown in the following image:
Make sure you leave the free tier selected, as shown in the following image:
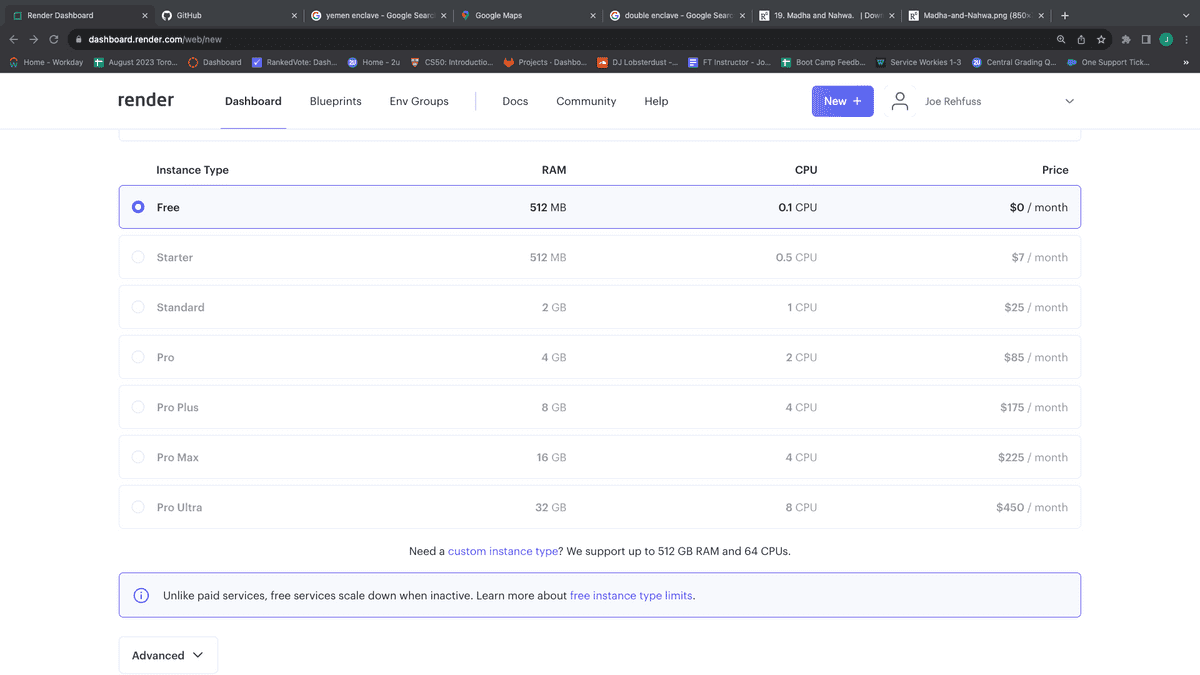
Next, click the "Create Web Service" button, as shown in the following image:
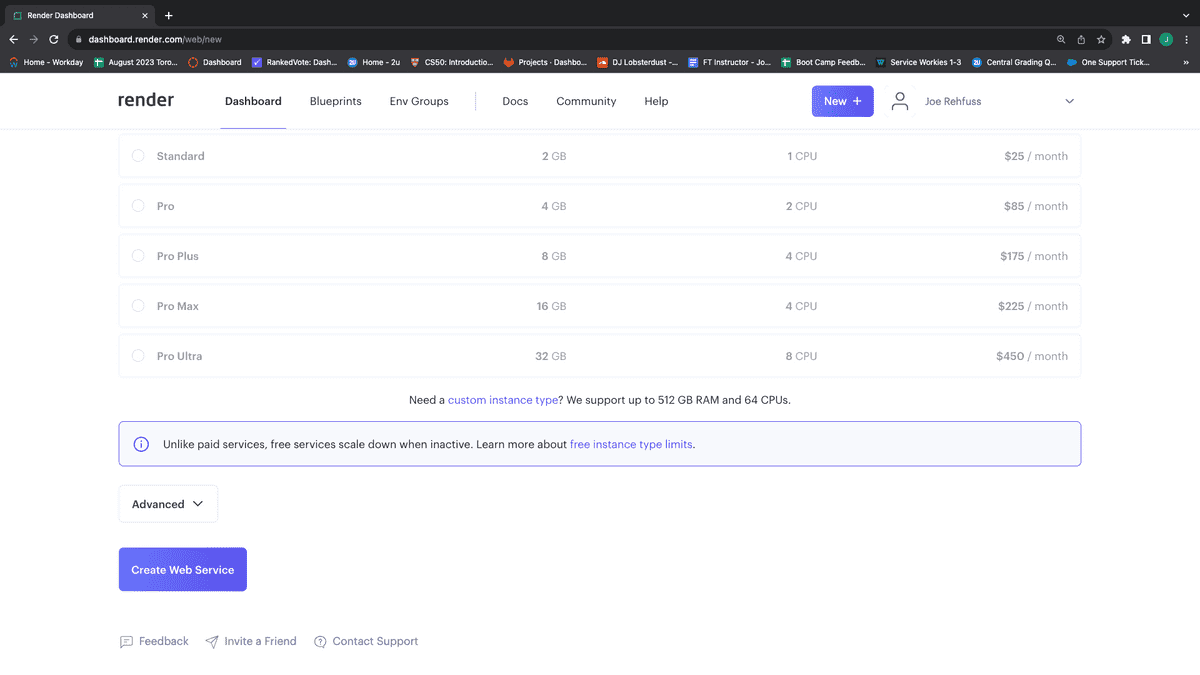
The next page will log all the actions being taken to set up your server. Once your server goes live, you can use the provided link toward the top of the page to view your live site, as shown in the following image:
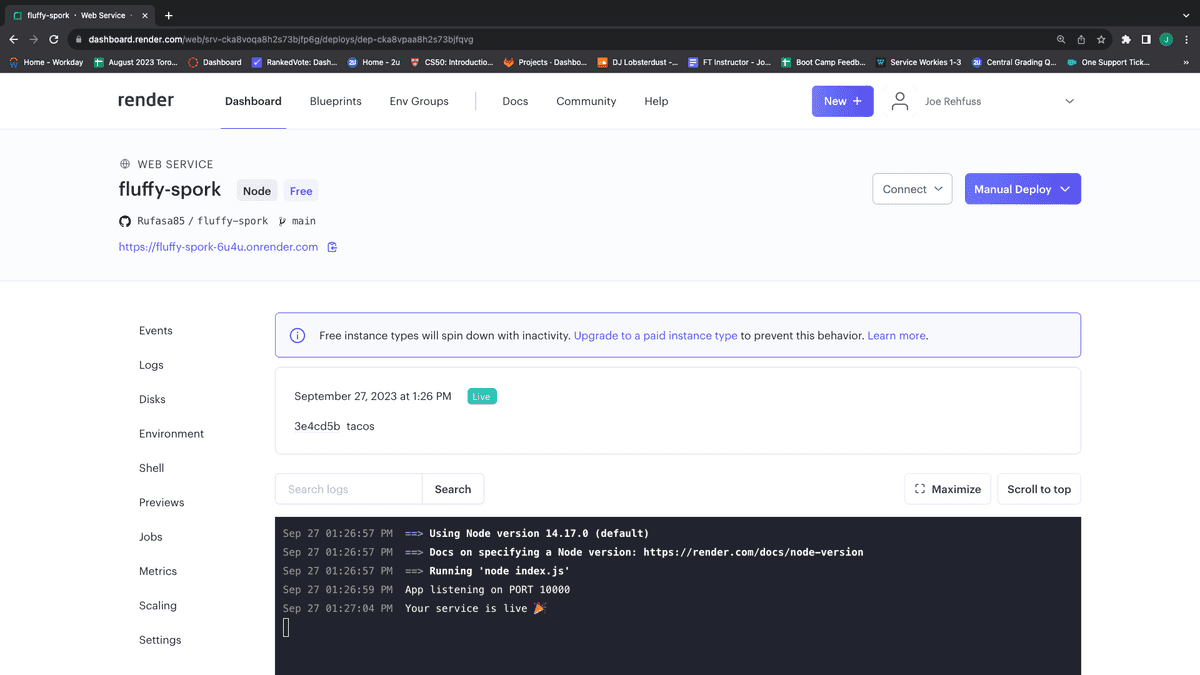
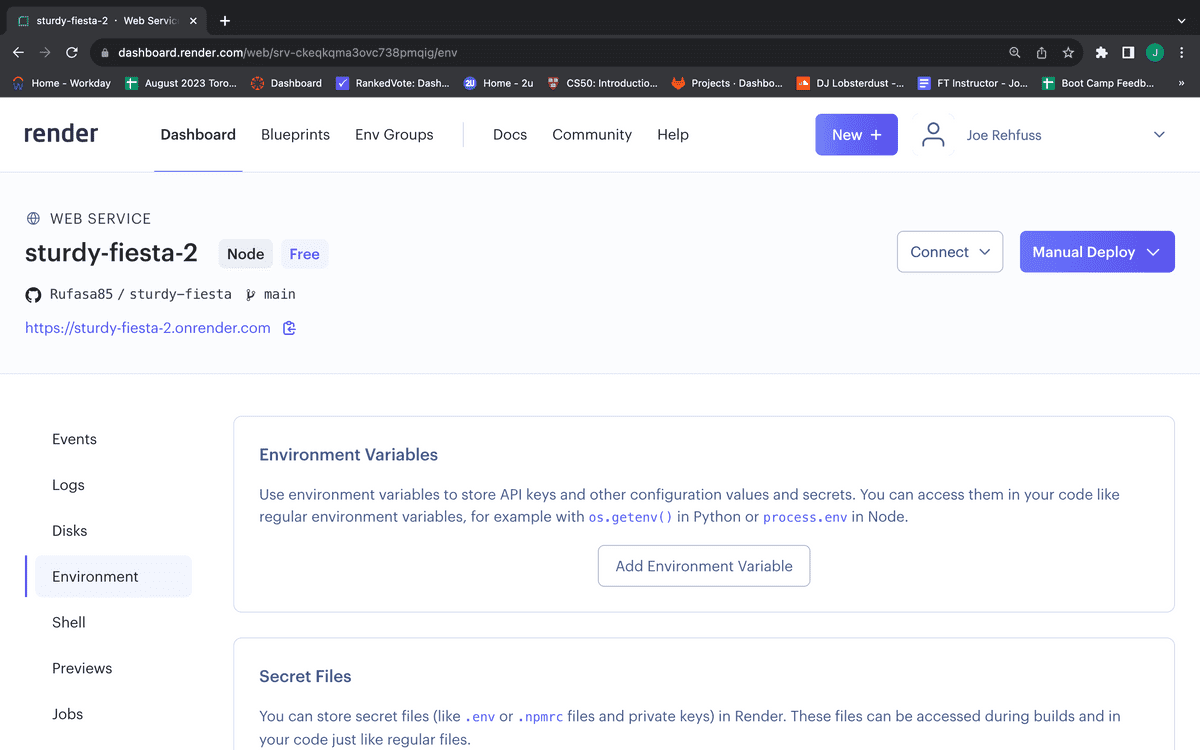
Clicking the "Environment" link takes you to a page where you can set your environment variables, as shown in the following image:
Open your MongoDB Atlas dashboard in another browser tab so you don't leave the Render page. Once there, locate the Connect button in your cluster's information and click it. If you're having trouble finding it, refer to the following image:
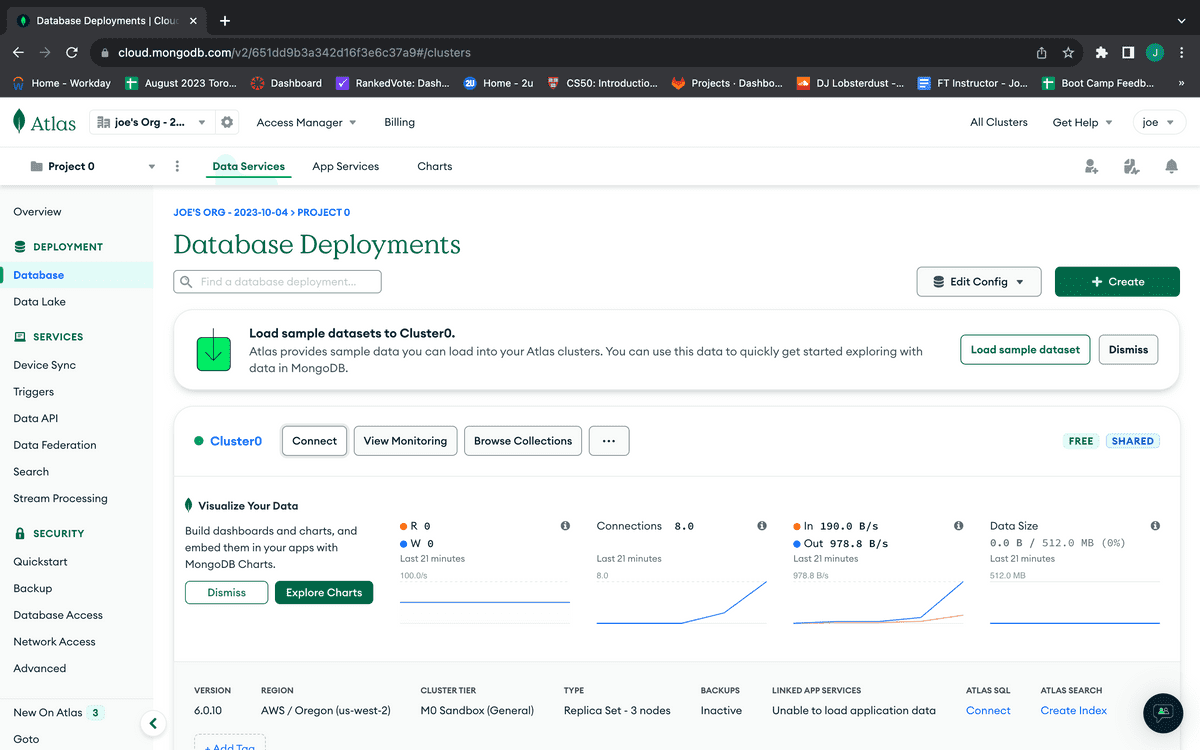
When the connection modal dialog opens, you should see the options shown in the following image:
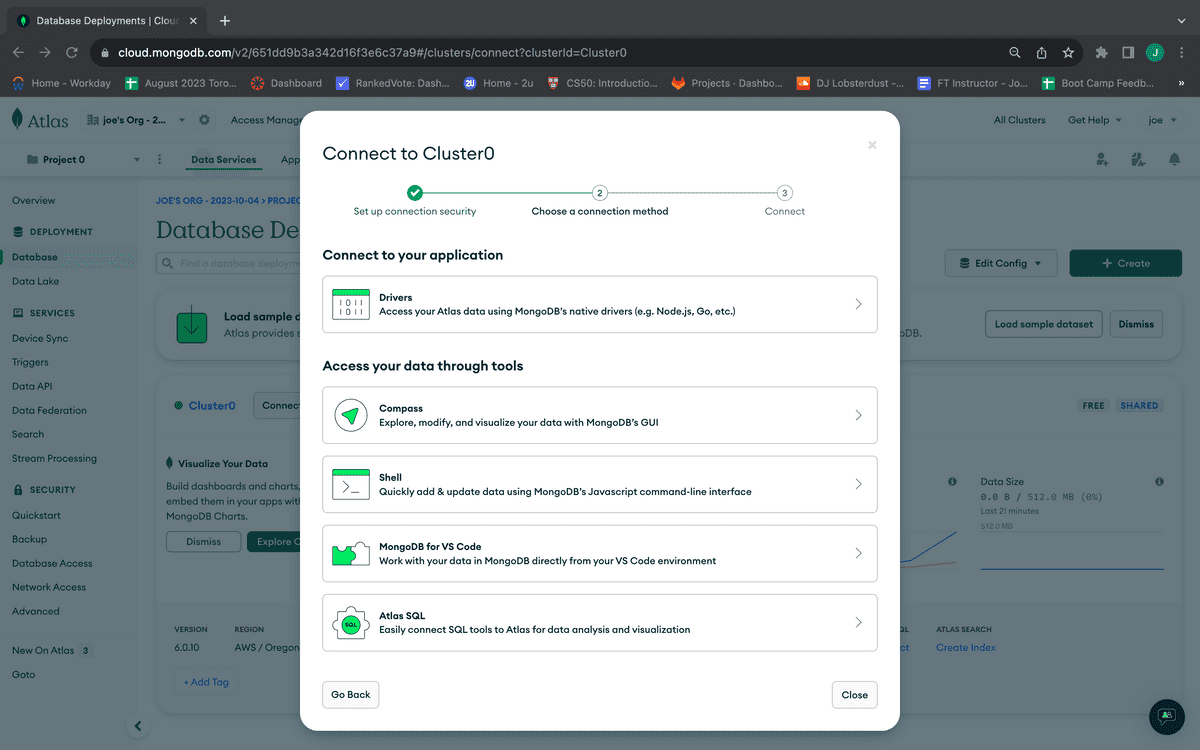
Because you want to connect our database to an application, select the first option, "Drivers," under the header "Connect your application." You'll then see something like the following image:
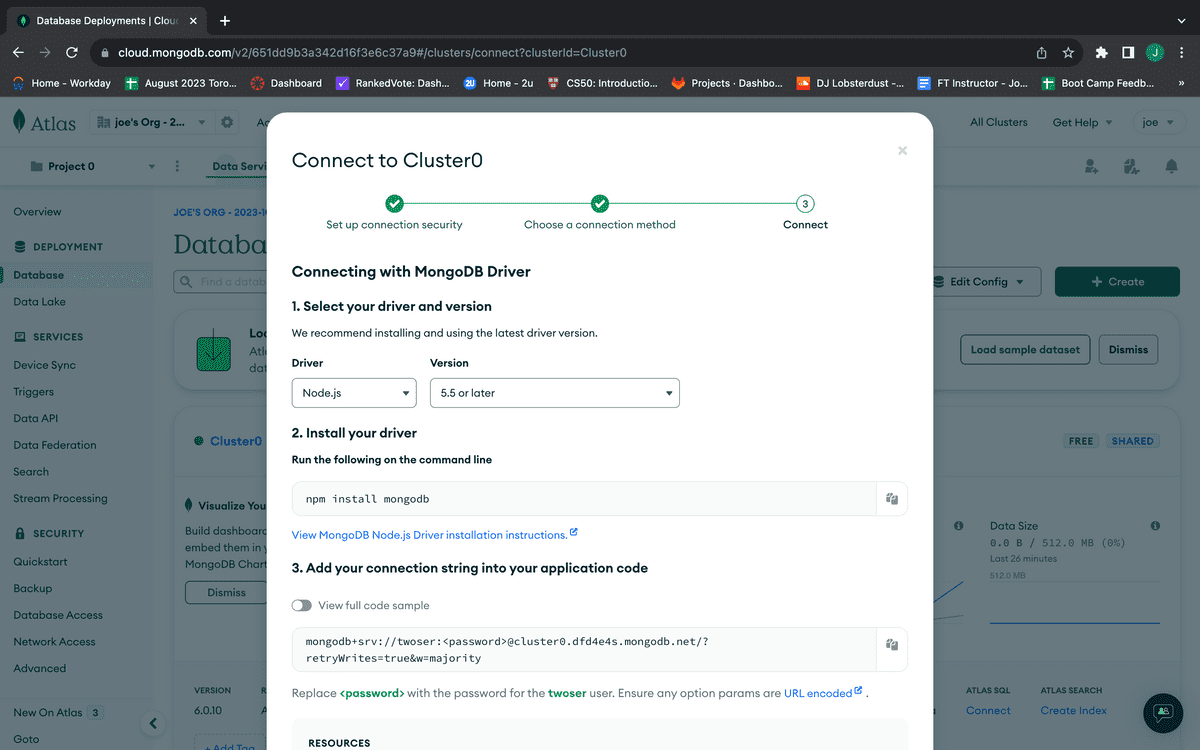
Here, all you need to do is copy the connection string listed in the second step. So go ahead and click the Copy button.
With the connection string copied, navigate back to your Render application settings.
Click the "Add Environment Variable" button, add a key named MONGODB_URI and paste the value of the connection string.
We need to update the connection string to include our database name, username, and password. The URL connection string should look like the following code:
mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@cluster0.5k55w.mongodb.net/<dbname>?retryWrites=true&w=majority
By default, MongoDB Atlas will populate your database username and leave off the database name, as shown in the following code:
mongodb+srv://twoser:<password>@cluster0.dfd4e4s.mongodb.net/?retryWrites=true&w=majority
Update the string so your password is correct and make sure to add the database name where <dbname> is indicated above, as shown in the following code:
mongodb+srv://twoser:password1234@cluster0.5k55w.mongodb.net/firstdb?retryWrites=true&w=majority
Note Make sure you're using the database user password, and not your MongoDB Atlas account password.
Click the "Save Changes" button to apply the changes, as shown in the following image:
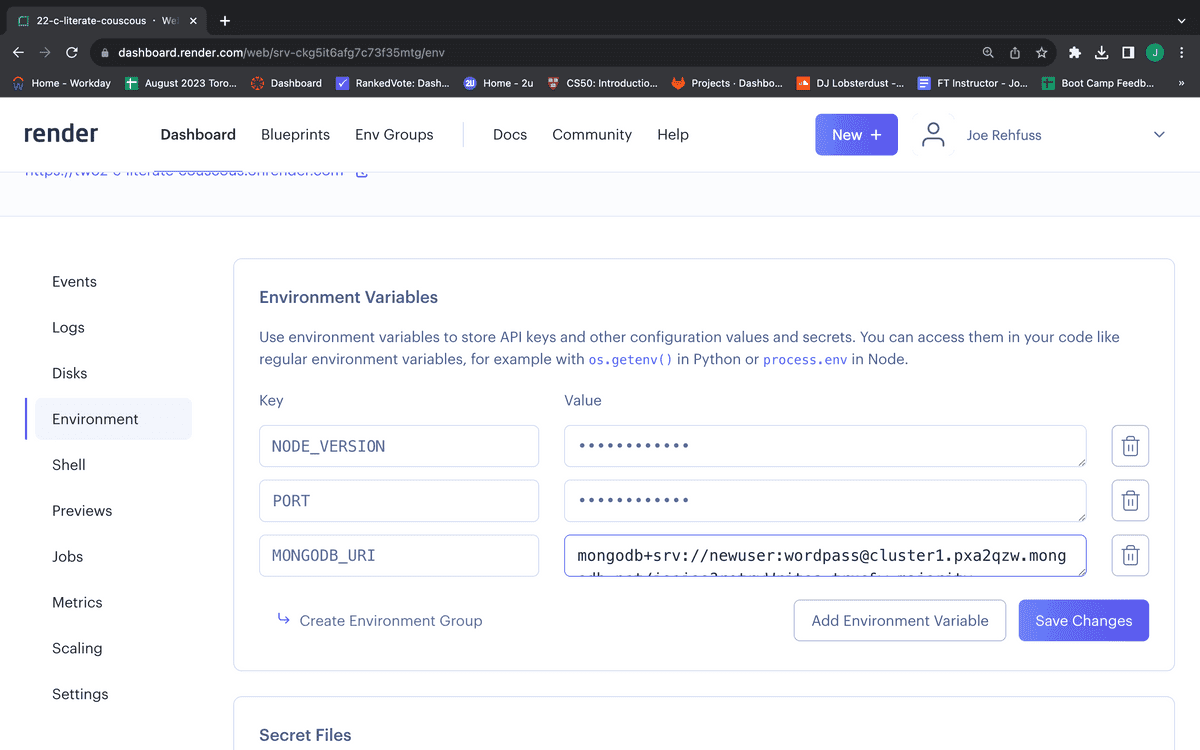
Finally, you can click the "Logs" link and use the provided link toward the top of the page to view your live site, as shown in the following image:

In order to seed your deployed Render application. We will need to run our seed script to our Atlas database. Typically, our hosting solution would allow us to run a shell command to complete this process, but the Render free tier does not allow for shell access, so we will need a workaround.
Navigate to your Render environment variables and copy the Mongo Atlas connection string, as shown in the following image:

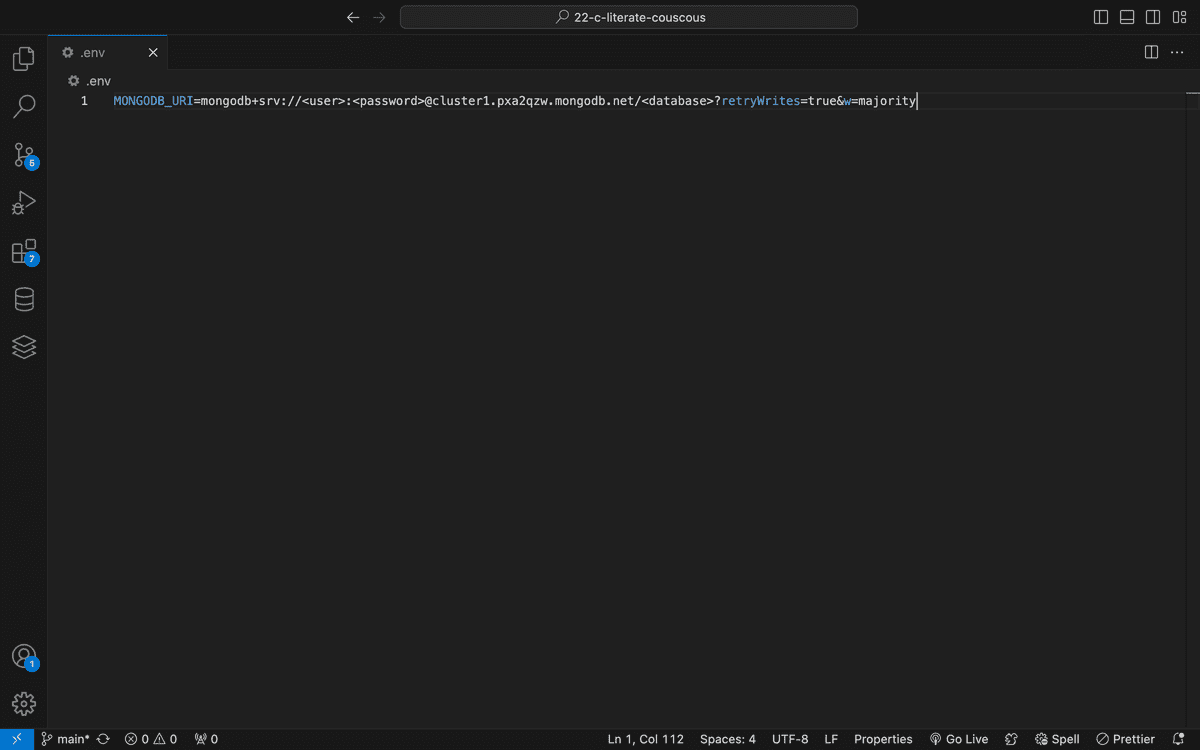
In the root level of your application, create a .env file and add the key of MONGODB_URI with the value of your Atlas database string, as shown in the following image. (Note that placeholders are used in this screenshot for database user, password, and name):
Change directory into the server folder of your application and install the dotenv package:
cd servernpm install dotenv
We need to enable environment variables to allow us to connect to our deployed database. As the following line the top of the server/config/connection.js file:
require("dotenv").config();
Change directory back to the root level of your application:
cd ..
Update the package.json file at the root of your repository so that the seed script directly runs the seed file (this is to ensure the environment variables are processed correctly), as shown in the following example:
"seed": "node server/config/seeds.js",
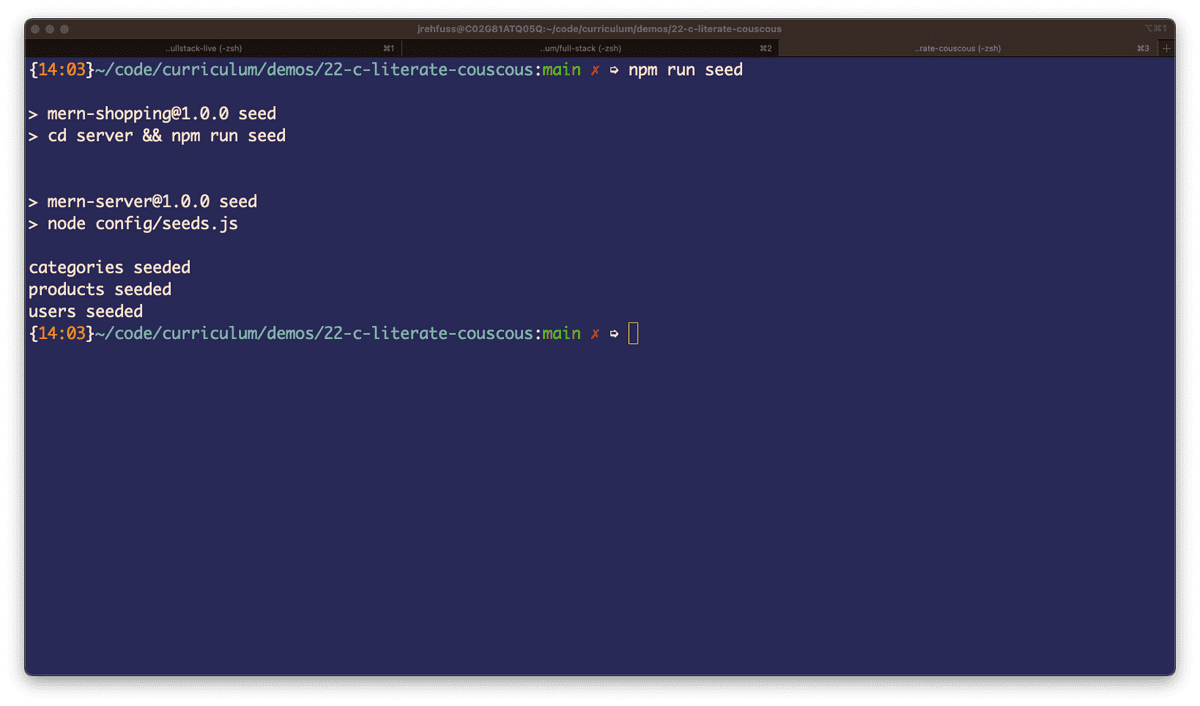
Run the npm run seed command from the root level of your application, as shown in the following image:
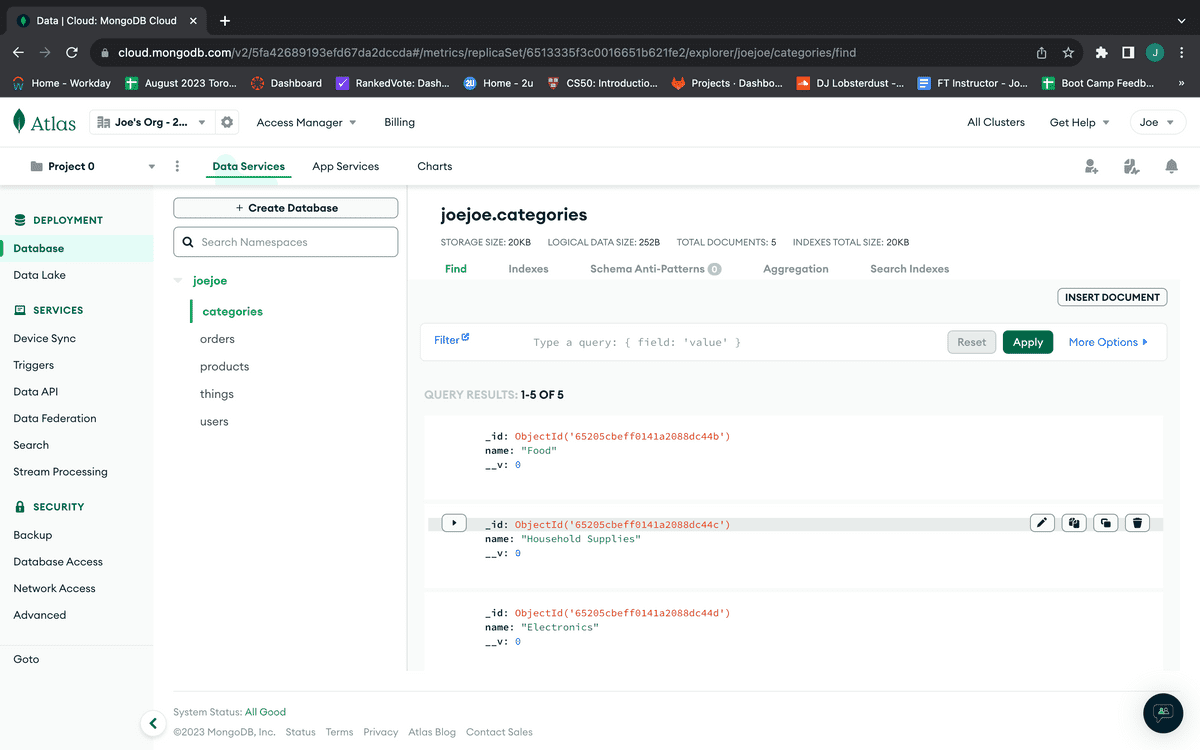
To confirm the data was successfully seeded, click on the "Browse Collections" button on your Mongo Atlas Dashboard. You should see some seeded data in your database, like the following image:
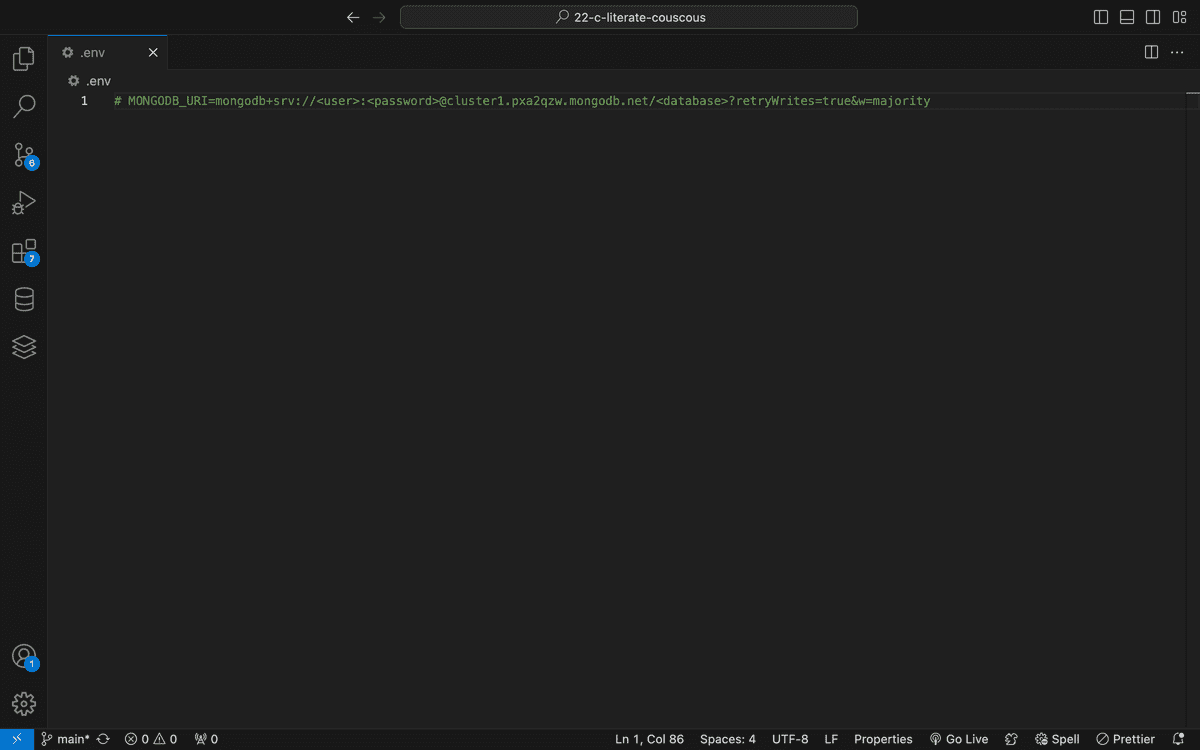
Finally, be sure to are only connecting to your Mongo Atlas database when necessary, comment out the MONGODB_URI in your .env file:
Visit the following link to supplement this guide:
This page was updated 2 months ago
© 2022 edX Boot Camps LLC. Confidential and Proprietary. All Rights Reserved.
Category: render
Tagged under: render, MERN, deployment, guide,
All Posts
- OpenAI Account Setup Guide
- NodeJS Installation Guide
- PostgreSQL Reference Guide
- GitHub Copilot Guide
- PostgreSQL Installation Guide
- Deploy with Render and PostgreSQL
- API Resources
- Render Deployment Guide
- Deploying a MERN Stack Application to Render
- Deploy with Render and MongoDB Atlas
- The Science and Research Behind Our Unconventional Educational Approach
- What Makes Up a Web Development Project?
- Localhost Loopback Issues Troubleshooting Guide
- Video Submission Guide
- A Growth Mindset for Life
- Web Literacy
- Developer Resources
- Introduction to Computer Structure and Organization
- MySQL Installation Guide
- HTML Cheatsheet
- Advanced Computer Skills
- Introduction to Computer Skills
- How to Use API Keys
- How to Install MongoDB
- MySQL Reference Guide
- Heroku Deployment Guide
- Getting Started with Git
- Using the GraphQL Playground in a MERN application
- Professional README Guide
- Regular Expression Tutorial
- How to Install the Heroku CLI
- How to Install NodeJS
- Deploy with Heroku and MySQL
- Deploy with Heroku and MongoDB Atlas
- Set Up MongoDB Atlas